Skin Cancer Surgical Center
Our Skin Cancer Surgical Center is one of the largest in Georgia. We are proud to help patients address a variety of skin cancer conditions with advanced and effective treatment techniques.
What is Skin Cancer?
Cancer occurs when the body’s cells cease to grow in an organized and normal fashion. When cancer cells are present, it’s possible for them to spread from one part of the body to another through the blood, lymph, or nervous system. This process is known as metastasis. Goodman Dermatology offers medical, surgical, and cosmetic therapies for patients with cancers of the skin.
Skin cancer may include basal cell carcinoma, the most commonly diagnosed form; squamous cell carcinoma; or melanoma. Each of these cancers has different symptoms, and treatment options differ for each type. The patient is evaluated, diagnosed, and provided with appropriate next steps for treatment.
What Causes Skin Cancer? Can I Prevent It?
Skin cancer is actually quite preventable. Patients who avoid harmful ultraviolet light (UVA and UVB rays) can help to keep their skin healthy. The sun is the primary source of this kind of radiation, but some patients use dangerous tanning salons or tanning beds. The American Cancer Society strongly discourages the use of tanning machines because they’re known to promote cancer.
It’s important for patients to protect their skin with clothes and sunscreen when they choose to spend time in the sun. Sunburns, especially those suffered in the patient’s early life, have been shown to increase his or her potential to develop skin cancer later on.
Light or fair skin and Caucasian race is another risk factor for skin cancer. Melanin, a pigment present in all skin, helps to protect the patient’s skin from UV damage. Darker skinned patients have more melanin present, so they’re at lower risk for the development of epidermal cancer. Of course, lower risk doesn’t mean “no risk,” so all patients should use sunscreen and wear protective clothes when enjoying the sun.
Other risk factors for skin cancer, such as a prior incidence of skin cancer; genetic likelihood (family history) of skin cancer; radiation treatment for any other form of cancer; psoriasis treatments using special UV lights; environmental proximity of the body to certain chemicals, including petroleum, arsenic, or tar; poor immune function; smoking cigarettes; scarring from prior skin infections or burns; other skin disease, such as basal cell nevus syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum; abnormal moles; human papilloma virus (HPV) infections; and more.
Why Choose Us?
Our Board Certified Dermatologist, Dr. Christopher Buckley’s primary focus of practice is Mohs Micrographic, reconstructive and cosmetic surgery and has performed over 23,000+ plus cases in his career so far. In addition to being a board-certified Dermatologist and fellowship-trained Mohs Surgeon, Dr. Buckley is a Diplomat of the American Osteopathic Board of Dermatology and a Fellow of both the American Academy of Cosmetic Surgery and the American Osteopathic College of Dermatology. He is a member of the American College of Mohs Surgery, American Academy of Dermatology, American Society for Dermatologic Surgery, American Society of Cosmetic Dermatology and Aesthetic Surgery, American Osteopathic Association, and numerous others.
What Are the Types of Skin Cancer?
The American Cancer Society reports that skin cancer diagnoses continue to increase each year. Approximately one million residents of the U.S. are told they have at least one form of skin cancer: it’s possible for a patient to have all three types of skin cancer present. These serious conditions require treatment. Dr. Marcus B. Goodman evaluates, diagnoses, and treats patients with skin cancer and all types of human skin disease or condition.
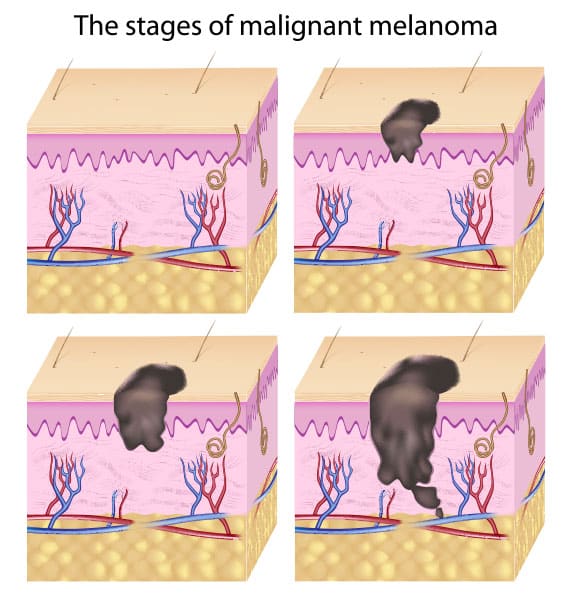
Basal Cell Carcinoma continues to be the most often diagnosed form of skin cancer (about seventy-five to eighty percent of all s cancer diagnoses are this form). These lesions present in the skin’s top layer, frequently on the neck, hands, and face where skin has been exposed to damaging UV rays of the sun. This type of skin cancer is often the most treatable because it’s least likely to spread from one part of the body to another.
Any skin cancer can spread, however, and even basal cell carcinoma can cause the sufferer to feel disfigured. It’s possible to lose fingers, eyes, nose, or even ears as a result of the growth of this cancer type. Patients should report any lesion that bleeds or oozes; turns red quite suddenly; or looks a bit like a scar (a bump may or may not be present). These lesions can be skin cancer. For more in-depth information about Basal Cell Carcinoma, click here.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma is diagnosed in about twenty percent of epidermal cancer cases. Men develop Squamous cell carcinoma about twice as often as women. American Cancer Society says that almost three hundred thousand cases of this type of cancer are diagnosed each year, and that the numbers of cases are rising. Patients usually see this form of epidermal cancer on the face, hands, neck, lips, or ears. Sometimes, the lesion becomes an open sore that won’t heal. Other times, it’s red or flat, develops scales or a crusty appearance. In other instances, a raised bump appears and continues to grow. Squamous cell carcinoma has the potential to spread from one location to the patient’s bones and organs. These tumors are usually small and thin at first, and most are successfully treated if identified early. About one percent of those diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma die from the disease. To learn more about Squamous Cell Carcinoma, click here.
Abnormal Moles are moles that can become cancer. Researchers from Johns Hopkins University cite the ABCD acronym for identifying moles that can be abnormal or cancerous. Consider these indicators:
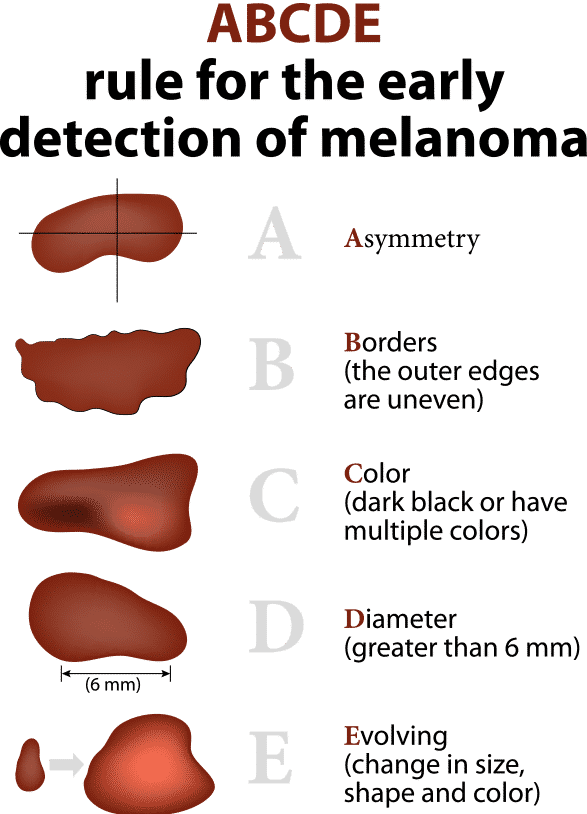
- Assymetry: An uneven shape can help the patient and physician identify an early problem. Not all assymetric moles are cancer but it’s important to perform self-checks and report any concerns to the doctor.
- Borders: An uneven, feathered, notched, or wavy border around any mole should be checked.
- Color: The mole’s color can be an early warning symptom. Most moles are a single color. When a mole is partially two or more colors, it’s time to call the dermatologist. Some very unusual colors, including blue, white, or black, may be early warning symptoms of a serious skin cancer called melanoma. For more information on melanoma, click here.
- Diameter: The mole’s width can help to identify a problem. When an existing mole grows quickly or appears and grows quickly, contact Goodman Dermatology. For more information about abnormal moles, click here.

How Does a Dermatologist Evaluate or Diagnose Skin Cancer?
The dermatologist will biopsy lesions before confirming diagnosis. Treatment is initiated after Goodman Dermatology confirms the diagnosis. There are a wide variety of treatments available to patients suffering from epidermal cancers, including topical treatments, chemotherapy or immunomodulator medications. Some epidermal cancers require surgical excision; others can be removed with laser therapies. The Skin Cancer Foundation reports that early identification and treatment are important to successful treatment. About eighty-five percent of patients with these cancers will recover with the benefit of physician’s care.
To learn more about skin cancer treatment or schedule your appointment at our Skin Cancer Surgical Center, contact us today. We serve the North Atlanta area, including Johns Creek, Jasper and Woodstock, Georgia.
